How Automation And Private 5G Help Drive Smart Manufacturing
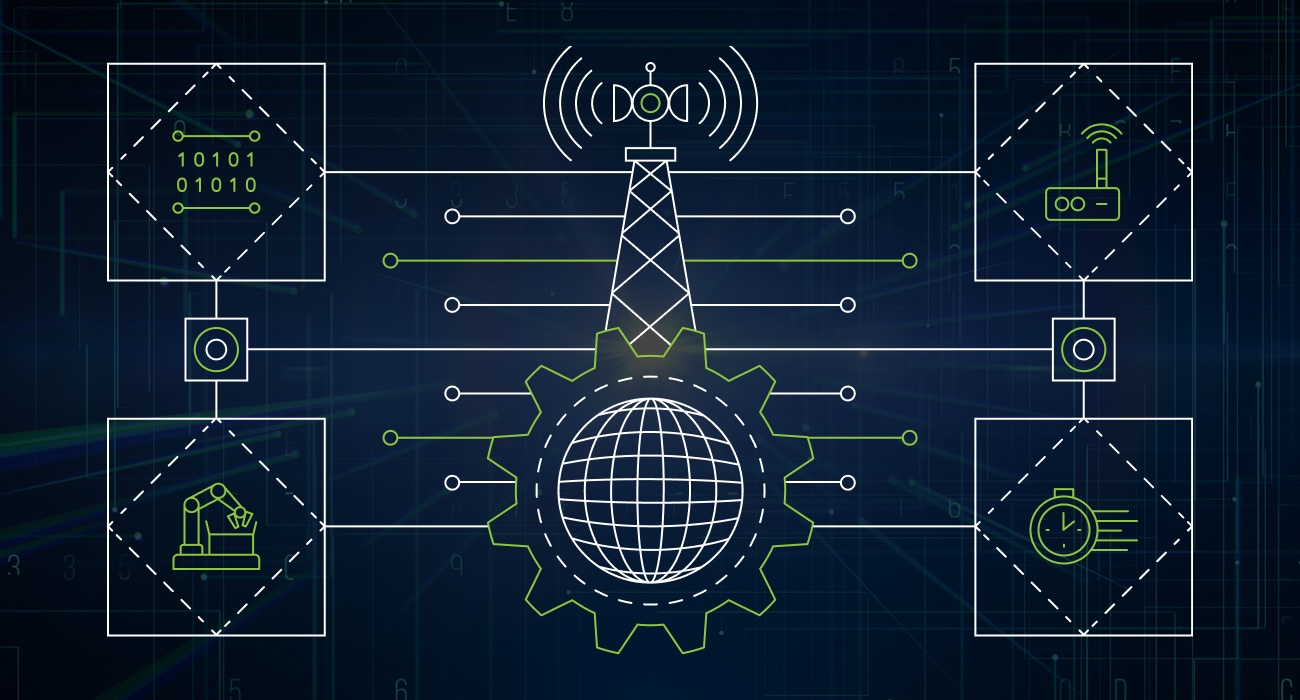
The manufacturing industry is experiencing a transformation driven by the convergence of advanced technologies. At the heart of this revolution is smart manufacturing, a concept that leverages data-driven insights to optimize production processes, improve product quality, and enhance innovation. This transformation is fueled by advanced analytics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and automation, all of which require robust connectivity to function effectively.
That’s where private 5G networks find a foothold. Private 5G promises to redefine how manufacturing operations are conducted by providing low-latency, reliable, and secure connectivity.
Why Smart Manufacturing and Private 5G Need Each Other
Smart manufacturing relies heavily on data. Advanced analytics allows manufacturers to process vast datasets to predict trends, optimize processes, and uncover growth opportunities. However, traditional data systems and networks often fall short in capturing, storing, and processing the immense volumes of data generated on the plant floor.
The connectivity challenges faced by traditional networks underscore the need for a more reliable solution in manufacturing environments. Ethernet connectivity requires cabling, which is restrictive for mobile assets. Legacy Wi-Fi systems can lack scalability and flexibility, or the low latency necessary for real-time data access — presenting a barrier to fully realizing the benefits of advanced analytics. Plus, decent coverage with Wi-Fi requires a significant investment in access points. Public cellular connectivity is better, but enterprises have little control over quality of experience.
Private 5G networks excel in maintaining seamless and secure communication across the entire facility, from the plant floor to on-site staff and headquarters. They enable bi-directional data flow, facilitating real-time data exchange and control, which is vital for supporting advanced applications like remote monitoring and automation.
The reliability, low latency, and security of private 5G networks enable manufacturers to efficiently handle large volumes of data generated by industrial IoT devices. Consistent connectivity ensures uninterrupted data collection from all areas, while low latency allows for swift data transmission and processing. This enables real-time decision-making, optimizing production processes, enhancing product quality, and accelerating decision-making. By connecting key stakeholders and systems, private 5G networks empower manufacturers to make informed, data-driven decisions quickly.

The Future Of Automation In Industry 4.0 Scenarios
Industry 4.0 is characterized by the integration of cyber-physical systems, IoT, and advanced analytics to create intelligent and automated environments. Automation plays a pivotal role in this landscape, allowing manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce manual intervention, and increase productivity.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and cyber-physical systems (CPS) exemplify the future of automation in manufacturing. AMRs, powered by AI and machine learning, can navigate complex environments, collaborate with human workers, and optimize material flow. CPS, on the other hand, enables intelligent control of complex systems by integrating sensing, computation, control, and networking.

The combination of private 5G networks and these advanced technologies creates a powerful foundation for Industry 4.0 applications, such as digital twins, augmented reality, and autonomous things. This convergence already is ushering in enhanced efficiency, improved flexibility, increased productivity, and new growth opportunities for manufacturers.
Examples Of Autonomous Things In Manufacturing
Smart robots: Industrial robots work autonomously, learning from human-supervised training and demonstrations conducted in short-term intervals.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs): AMRs utilize sensors and AI to navigate autonomously, delivering materials to workstations and optimizing production workflows.
Collaborative robots (Cobots): Designed to work alongside humans, Cobots can handle assembly, sorting, and packaging while promoting human-machine collaboration on the factory floor.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): UAVs can do aerial inspections in hard-to-reach and dangerous areas. Equipped with high-resolution cameras, UAVs can inspect machinery, buildings, and inventory.
Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs): These driverless vehicles follow magnetic strips, wires in the floor, or laser guidance systems. AGVs are ideal for transporting heavy materials over long distances.
Autonomous forklifts: These intelligent vehicles can navigate their environment, retrieve and transport pallets of materials, and even stack them on shelves autonomously. This reduces the risk of accidents associated with traditional forklifts and frees up human workers for higher-value tasks.
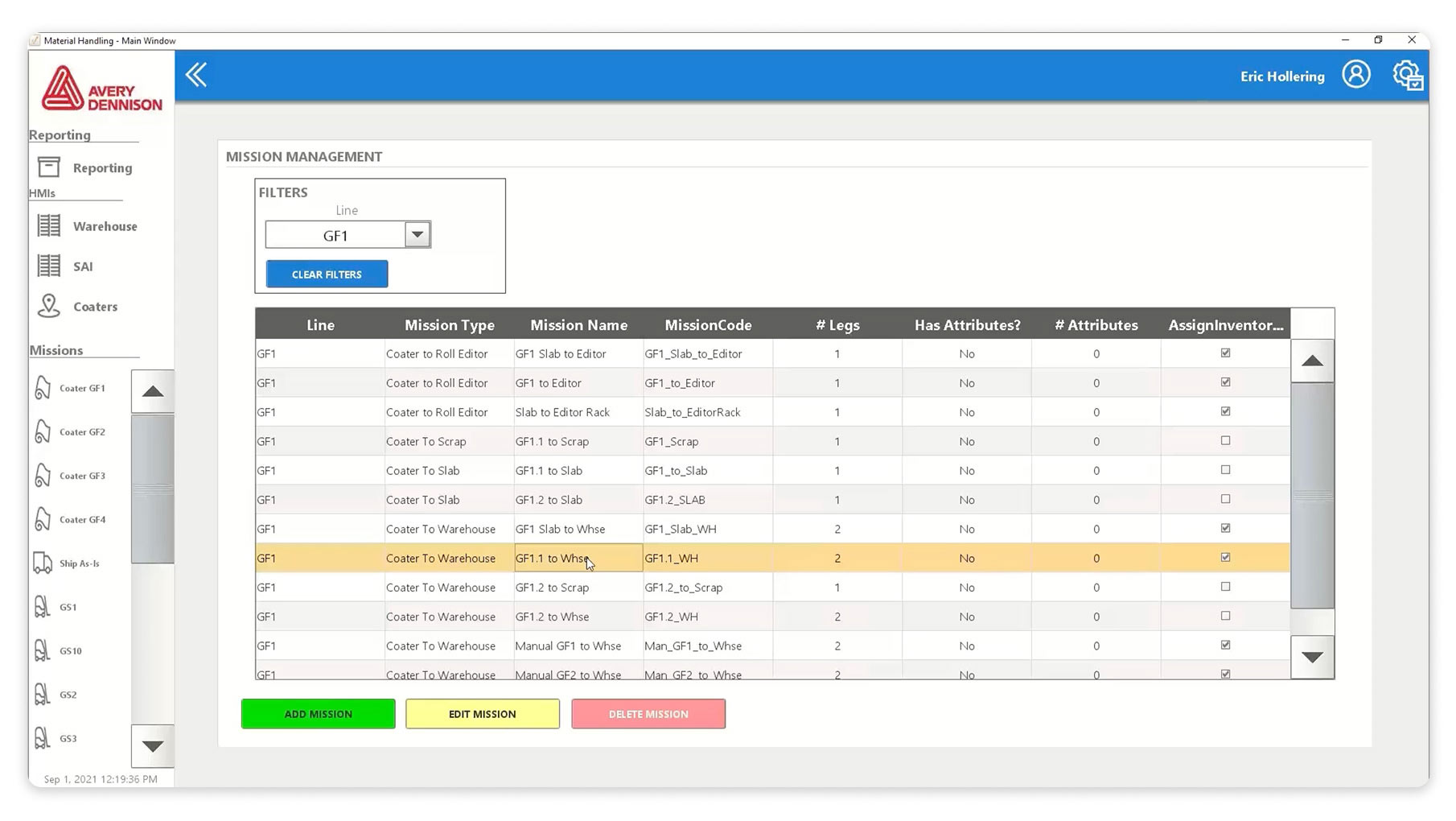
One example of these technologies in action is a project by Flexware Innovation for Avery Dennison. In its Greenfield, Indiana plant, Avery Dennison wanted to create a comprehensive material handling solution that would seamlessly integrate its new materials-transferring AGV system with existing facility systems and processes. Flexware utilized its Ignition-based Logistics Integration Framework Technology (LIFT) framework to create a fully integrated logistics solution and help make Avery’s expansion a success.

Enterprises Are Embracing Private 5G As Part Of Smart Manufacturing
Several companies already are harnessing the power of private 5G networks to drive smart manufacturing initiatives. Ericsson's collaboration with Calpak, a fully automated solar water heater production facility, showcases the benefits of predictive maintenance powered by advanced analytics and private 5G. By predicting equipment failures before they occur, Calpak can significantly reduce downtime, optimize maintenance schedules, and improve asset lifespan.
Hitachi Rail is building an advanced digital factory in the United States, leveraging private 5G to coordinate and connect a myriad of autonomous technologies. This effort demonstrates the potential of private 5G to enable seamless integration and operation of smart manufacturing systems.
In Sweden, a pilot project featuring autonomous electric trucks within a DB Schenker facility highlights how private 5G can revolutionize transportation. The reliable 5G connectivity provided by Ericsson and Telia ensures safe and efficient operation of these driverless vehicles.
Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) is using Ericsson Private 5G at its Solihull plant to enhance the production of Range Rover vehicles with business-critical applications such as vision systems, IoT sensors, and production tools. This is helping JLR set new standards in modern automotive manufacturing.

Ericsson Enterprise Wireless And Inductive Automation Help Make Smart Manufacturing Even Smarter
Integrating Inductive Automation's Ignition software with Ericsson Enterprise Wireless’ private 5G solution helps make smart manufacturing even ... smarter. Ignition, a universal industrial application platform, meets the demands of industrial loT (lloT) and automation by providing a scalable and secure environment for various applications — all of which require nonstop wireless connectivity.
The companies have worked together to enable Ignition to run in a container on an Ericsson router, streamlining deployment and saving on hardware costs.
Together, they provide a comprehensive solution tailored to meet the diverse needs of the manufacturing sector — needs such as effective remote monitoring and control across large facilities, allowing precise management to ensure uptime and enhance system responsiveness.
Ericsson participates in Inductive Automation’s Ignition Technology Ecosystem Program and Inductive Automation participates in Ericsson’s Technology Alliance Partners Program, which provides a foundation for ongoing innovation and collaboration.
